MXD1
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| MXD1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | MXD1, BHLHC58, MAD, MAD1, MAX dimerization protein 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 600021; MGI: 96908; HomoloGene: 1767; GeneCards: MXD1; OMA:MXD1 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MAD protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MXD1 gene.[5][6]
MAD-MAX dimerization protein belongs to a subfamily of MAX-interacting proteins. This protein competes with MYC for binding to MAX to form a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex, acts as a transcriptional repressor (while MYC appears to function as an activator) and is a candidate tumor suppressor.[6]
Interactions
MXD1 has been shown to interact with Histone deacetylase 2,[7][8] SMC3,[9] MLX,[10][11] SIN3A[12][13][14] and MAX.[9][15][16][17]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000059728 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000001156 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Shapiro DN, Valentine V, Eagle L, Yin X, Morris SW, Prochownik EV (February 1995). "Assignment of the human MAD and MXI1 genes to chromosomes 2p12-p13 and 10q24-q25". Genomics. 23 (1): 282–5. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1496. PMID 7829091.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: MXD1 MAX dimerization protein 1".
- ^ Laherty, C D; Yang W M; Sun J M; Davie J R; Seto E; Eisenman R N (May 1997). "Histone deacetylases associated with the mSin3 corepressor mediate mad transcriptional repression". Cell. 89 (3). UNITED STATES: 349–56. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80215-9. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 9150134. S2CID 13490886.
- ^ Spronk, C A; Tessari M; Kaan A M; Jansen J F; Vermeulen M; Stunnenberg H G; Vuister G W (December 2000). "The Mad1-Sin3B interaction involves a novel helical fold". Nat. Struct. Biol. 7 (12). UNITED STATES: 1100–4. doi:10.1038/81944. ISSN 1072-8368. PMID 11101889. S2CID 12451972.
- ^ a b Gupta, K; Anand G; Yin X; Grove L; Prochownik E V (March 1998). "Mmip1: a novel leucine zipper protein that reverses the suppressive effects of Mad family members on c-myc". Oncogene. 16 (9). ENGLAND: 1149–59. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201634. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 9528857.
- ^ Cairo, S; Merla G; Urbinati F; Ballabio A; Reymond A (March 2001). "WBSCR14, a gene mapping to the Williams--Beuren syndrome deleted region, is a new member of the Mlx transcription factor network". Hum. Mol. Genet. 10 (6). England: 617–27. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.6.617. ISSN 0964-6906. PMID 11230181.
- ^ Meroni, G; Cairo S; Merla G; Messali S; Brent R; Ballabio A; Reymond A (July 2000). "Mlx, a new Max-like bHLHZip family member: the center stage of a novel transcription factors regulatory pathway?". Oncogene. 19 (29). ENGLAND: 3266–77. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203634. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 10918583.
- ^ Swanson, Kurt A; Knoepfler Paul S; Huang Kai; Kang Richard S; Cowley Shaun M; Laherty Carol D; Eisenman Robert N; Radhakrishnan Ishwar (August 2004). "HBP1 and Mad1 repressors bind the Sin3 corepressor PAH2 domain with opposite helical orientations". Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11 (8). United States: 738–46. doi:10.1038/nsmb798. ISSN 1545-9993. PMID 15235594. S2CID 44324333.
- ^ Brubaker, K; Cowley S M; Huang K; Loo L; Yochum G S; Ayer D E; Eisenman R N; Radhakrishnan I (November 2000). "Solution structure of the interacting domains of the Mad-Sin3 complex: implications for recruitment of a chromatin-modifying complex". Cell. 103 (4). UNITED STATES: 655–65. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00168-9. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 11106735. S2CID 17476603.
- ^ Ayer, D E; Lawrence Q A; Eisenman R N (March 1995). "Mad-Max transcriptional repression is mediated by ternary complex formation with mammalian homologs of yeast repressor Sin3". Cell. 80 (5). UNITED STATES: 767–76. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90355-0. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 7889570. S2CID 8749951.
- ^ Lee, Clement M; Onésime Djamila; Reddy C Damodara; Dhanasekaran N; Reddy E Premkumar (October 2002). "JLP: A scaffolding protein that tethers JNK/p38MAPK signaling modules and transcription factors". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (22). United States: 14189–94. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9914189L. doi:10.1073/pnas.232310199. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 137859. PMID 12391307.
- ^ Ayer, D E; Kretzner L; Eisenman R N (January 1993). "Mad: a heterodimeric partner for Max that antagonizes Myc transcriptional activity". Cell. 72 (2). UNITED STATES: 211–22. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90661-9. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 8425218. S2CID 13317223.
- ^ Nair, Satish K; Burley Stephen K (January 2003). "X-ray structures of Myc-Max and Mad-Max recognizing DNA. Molecular bases of regulation by proto-oncogenic transcription factors". Cell. 112 (2). United States: 193–205. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01284-9. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 12553908. S2CID 16142388.
Further reading
- Grandori C, Cowley SM, James LP, Eisenman RN (2001). "The Myc/Max/Mad network and the transcriptional control of cell behavior". Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 16 (1): 653–99. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.653. PMID 11031250.
- Lüscher B (2001). "Function and regulation of the transcription factors of the Myc/Max/Mad network". Gene. 277 (1–2): 1–14. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00697-7. PMID 11602341.
- Ayer DE, Lawrence QA, Eisenman RN (1995). "Mad-Max transcriptional repression is mediated by ternary complex formation with mammalian homologs of yeast repressor Sin3". Cell. 80 (5): 767–76. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90355-0. PMID 7889570. S2CID 8749951.
- Edelhoff S, Ayer DE, Zervos AS, et al. (1994). "Mapping of two genes encoding members of a distinct subfamily of MAX interacting proteins: MAD to human chromosome 2 and mouse chromosome 6, and MXI1 to human chromosome 10 and mouse chromosome 19". Oncogene. 9 (2): 665–8. PMID 8290278.
- Ayer DE, Kretzner L, Eisenman RN (1993). "Mad: a heterodimeric partner for Max that antagonizes Myc transcriptional activity". Cell. 72 (2): 211–22. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90661-9. PMID 8425218. S2CID 13317223.
- Hassig CA, Fleischer TC, Billin AN, et al. (1997). "Histone deacetylase activity is required for full transcriptional repression by mSin3A". Cell. 89 (3): 341–7. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80214-7. PMID 9150133. S2CID 14233219.
- Laherty CD, Yang WM, Sun JM, et al. (1997). "Histone deacetylases associated with the mSin3 corepressor mediate mad transcriptional repression". Cell. 89 (3): 349–56. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80215-9. PMID 9150134. S2CID 13490886.
- Gupta K, Anand G, Yin X, et al. (1998). "Mmip1: a novel leucine zipper protein that reverses the suppressive effects of Mad family members on c-myc". Oncogene. 16 (9): 1149–59. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201634. PMID 9528857.
- FitzGerald MJ, Arsura M, Bellas RE, et al. (1999). "Differential effects of the widely expressed dMax splice variant of Max on E-box vs initiator element-mediated regulation by c-Myc". Oncogene. 18 (15): 2489–98. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202611. PMID 10229200.
- Khan MM, Nomura T, Kim H, et al. (2001). "Role of PML and PML-RARalpha in Mad-mediated transcriptional repression". Mol. Cell. 7 (6): 1233–43. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00257-X. PMID 11430826.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Nikiforov MA, Popov N, Kotenko I, et al. (2003). "The Mad and Myc basic domains are functionally equivalent". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (13): 11094–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212298200. PMID 12538578.
- Nair SK, Burley SK (2003). "X-ray structures of Myc-Max and Mad-Max recognizing DNA. Molecular bases of regulation by proto-oncogenic transcription factors". Cell. 112 (2): 193–205. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01284-9. PMID 12553908. S2CID 16142388.
- Siegel PM, Shu W, Massagué J (2003). "Mad upregulation and Id2 repression accompany transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta-mediated epithelial cell growth suppression". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (37): 35444–50. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301413200. PMID 12824180.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Hillier LW, Graves TA, Fulton RS, et al. (2005). "Generation and annotation of the DNA sequences of human chromosomes 2 and 4". Nature. 434 (7034): 724–31. Bibcode:2005Natur.434..724H. doi:10.1038/nature03466. PMID 15815621.
- Zada AA, Pulikkan JA, Bararia D, et al. (2007). "Proteomic discovery of Max as a novel interacting partner of C/EBPalpha: a Myc/Max/Mad link". Leukemia. 20 (12): 2137–46. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2404438. PMID 17082780.
External links
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: Q05195 (Max dimerization protein 1) at the PDBe-KB.
- v
- t
- e
PDB gallery
-
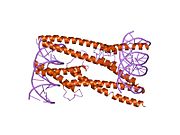 1nlw: Crystal structure of Mad-Max recognizing DNA
1nlw: Crystal structure of Mad-Max recognizing DNA