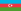
Talysh Khanate
Under Iranian suzerainty[1]

Talysh Khanate at its greatest extent (1826–1828)
| Preceded by | Succeeded by | ||||||||
|
|
Azerbaijan
Part of a series on the | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Iran | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prehistoric period BCE / BC
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CE / AD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related articles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Timeline Iran portal Iran portal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Talysh Khanate or Talish Khanate (Persian: خانات تالش, romanized: Khānāt-e Tālesh) was an Iranian khanate of Iranian origin that was established in Afsharid Persia and existed from the middle of the 18th century till the beginning of the 19th century, located in the south-west coast of the Caspian Sea.
It comprised the southeastern part of the modern-day Republic of Azerbaijan and the eastern tip of north-western Iran. The capital of the khanate was its chief city, Lankaran. As a result of the Persian defeat in the Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828, the khanate was dissolved and absorbed by the Russian Empire.
The uncertainty surrounding the history of Talysh Khanate is not due only to the paucity of sources, a further problem is the rarity of studies about it. Several studies and short surveys appeared in Russian, Azerbaijani, Turkish, and Persian. Regrettably, some of these studies are tenuous and contain erroneous and biased interpretations.[3]
Historiography
Because of the paucity of primary sources, the study of the Talysh Khanate faces serious obstacles. The primary sources for the study of the Khanate are roughly divided into three groups: chronicles, documentary material, and travel accounts.[4] Many facts related to the history of the Khanate are scattered throughout various chronicles produced by local and Qajar historians.[3]
The first Persian chronicle about the Talysh Khanate is Javāher Nāmeh-ye Lankarān (1869) (i.e., The Jewel Book of Lankaran[5]), written by Saeid-Ali ibn Kazem Beg Borādigāhi (1800–1872). There are two copies of The Jewel Book of Lankaran, and both are retained at the Institute of Manuscripts of Azerbaijan.[3] The second Persian chronicle is Akhbār Nāmeh (1882) (i.e., The Chronicle), written by Mirza Ahmad ibn Mirza Khodāverdi, whose father served as the vizier for the second and the third Khans of Talysh.[3]
Another primary source that may be added to the chronicle-type sources is the Russian survey entitled The History of the Talysh Khanate (1885) written by Teymur Bayramalibeyov (1863–1937).[3]
A nonspecific but relevant chronicle which written in Persian is Gulistan-i Iram (1845) (i.e., The Heavenly Rose-Garden) from Abbas-Qoli Aqa Bakikhanov (1794–1847). Although not dealing directly with the Talysh Khanate, it contains useful information on the region up to the year in which it was completed.[3]
The major body of correspondence of the Khans of Talysh is preserved in Russian archives and has been published in various collections of documents. The most important of these collections is the Acts collected by the Caucasian Archaeographic Commission (1866–1886).[3]
Travelogues and reports by merchants, agents, and informers, are another type of primary source that is potentially useful for the study of the Talysh Khanate. Among this type of source, one may mention accounts written by two Poles in Russian service: Jan Potocki (1761–1815), and Aleksander Chodźko (1804–1891). Another account relating to Talysh, is a report made by Camille Alphonse Trézel (1780–1860), a French officer who served under Claude-Matthieu Gardane (1766–1818), Napoleon's envoy to the Persian court.[3]
Background
In Safavid era, the population of Safavid Talish was a mixture of Iranian and Turkic elements. Generally, the Talyshis, an ethnic group speaking the Iranian language of Talysh, were Indigenous people of the region.[6] At the end of the 15th century, many Talysh leaders provided solid support to the Safavids, who rewarded them with honours and land. Theoretically, the local rulers were not hereditary lords.[6]
Khansuvarov believed that Mir Abbas was the grandson of Seyyed Abbas. His father's name was Seyyed Yūsef, who succeeded his grandfather in religious affairs. Seyyed Yūsef was buried at Yuxarı Nüvədi village of Lankaran.[7]
Administration
The Talysh region comprised lands in the southwestern part of the current Republic of Azerbaijan, as well as some territories in modern Iran. The exact definition of Talysh boundaries has varied over time. Present-day, Talysh is a mountainous region located between Gilan province and the Caspian Sea in the east and Ardabil province in the west. It is a narrow strip of land extending from Rudbar in the south to Astara in Iranian territory and on to the north of Lankaran District, located in the Republic of Azerbaijan. The northern half of Talysh is one of the seventeen provinces that were cut from Iranian territory as a result of the treaties of Gulistan (1813) and Turkmenchay (1828).[6]
The Talysh Khanate was bordered by the Gilan Khanate from the south, Ardabil Khanate from the southwest, Karadagh Khanate in the northwest, Javad Khanate from the north, and Salyan Sultanate from the north-east. Most of the eastern borders of the Khanate were bound to the Caspian Sea.[8]
Talysh Khanate was divided into administrative districts. According to the Saeid-Ali's book, there were eleven districts (Persian: محال, romanized: maḥāl) in the territory of the Khanate: Asalem (Persian: اسالم), Karganrud (Persian: کرگانرود), Astara[a] (Persian: آستارا), Vilkij[b] (Persian: ویلکیج), Zuvand (Persian: زووند), Chayichi-Lankaran (Persian: چایایچی-لنکران), Drigh[c] (Persian: دریغ), Uluf[d] (Persian: اُلوف), Dashtevand[e] (Persian: دشتوند), Sefiddasht[f] (Persian: سفید دشت), Ujarud[g] (Persian: اُجارود).
However, the territory of the Khanate did not always remain stable but underwent significant changes under the influence of various events.[8]
The largest territorial transformation in the Khanate took place during the Russo-Persian Wars. According to the treaties concluded between these states, all of Asalem, Karganrud and Vilkij districts and some parts of the Ujarud, Safidasht, Astara and Zuvand districts were given to Qajar Iran.[8]
History

According to Mirza Ahmad Mirza oglu Khudaverdi, the founder of the Talysh Khanate, Seyyid Abbas,[9] his ancestors were members of the Safavid dynasty, who had moved into the Talish region during the 1720s during a turbulent period in Iranian history. When Seyyid Abbas died in 1747 he was succeeded by his son Jamaladdin, often remembered as Gara Khan (the 'Black King'), because of his dark skin. Because of his good service to Nader Shah, Nader officially awarded him the hereditary title of khan.[10] Gara Khan was pro-Russian in his foreign policy which upset the rulers of neighbouring khanates notably Hidayat Khan of Gilan. In 1768 Hidayat Khan attacked the Talysh khanate. Seeking aid against the superior enemy, Gara Khan sent his brother Karbalayi Sultan to Fath Ali Khan, ruler of the Quba Khanate resulting in an alliance between Quba and Lankaran. By 1785 the territory of the Talysh khanate had formally become a dependency of that much stronger Quba Khanate together with certain other Azerbaijani khanates. However, in 1789 following Fath Ali Khan's death, the Talysh Khanate regained its independence under Mir Mustafa, the son of Gara Khan who had himself died in 1786.
In 1794–5 the Persian Shah Agha Mohammad Khan Qajar called on the various khanates of the South Caucasus to form an alliance against the Russian Empire and mounted a military expedition against those who refused to join him. The Talysh khanate refused to do and was attacked in 1795. Mir Mustafa Khan's disparate army was not strong enough to resist and he sent his representatives to General Gudovich asking for Russian protection. However, the Russians took a long time to respond, only finally arriving in 1802 when the Talysh Khanate became a protectorate of the Russian Empire.
The khanate was to remain a pawn between the Persian and Russian empires over the subsequent two decades. In 1809 as a part of the Russo-Persian War (1804–1813), Iranian troops took the city of Lankaran and expelled the Russian-leaning khan. In 1812, with Napoleon was attacking Moscow, the Russians were also battling again in the Caucasus. After a brief siege led by Pyotr Kotlyarevsky on January 1, 1813, 2,000 Russian troops managed to decisively take the citadel of Lenkaran from the Persian army. There were heavy losses on both sides, but this strategic capture of Lankaran led inexorably to September 12, 1813 Treaty of Gulistan. This forced defeated Persia to cede many of the formerly independent khanates to Russia. In 1814 Mir Mustafa khan died and his son Mir Hassan Khan succeeded him but only in name.
With Russia busy in European wars, Persia attempted to reassert its hegemony in the area and to revert the Treaty of Gulistan and thus invaded the south Caucasus, starting the 1826-28 Russo-Persian war. In the campaign of 1826, Persia managed to regain all lost territories, but after the numerous defeats in the campaign of 1827, the war ended up with the even more humiliating Treaty of Turkmenchay which permanently ceded the Talysh Khanate to Russia.
Yermolov took over the khanates of eastern Transcaucasia one by one and deposed their khans: Shaki in 1819, Shirvan in 1820, and Qara-Bagh in 1822. Only Mir Hassan Khan of Talesh was allowed autonomy, Ermolov understanding him and his family to be implacably hostile to Iran. In fact, Mir Hassan threw the Russians out in the year that hostilities reopened, and a strong Iranian force came to help him. He retained control of the khanate, in the name of the Shah, until he was forced to abandon it in 1828 by the Treaty of Turkmenchay.[2]
After Mir Hasan Khan's death, his children came under Abbas Mirza's patronage, with Mir Kazem Khan becoming the governor of Vilkij, Astara, Ujarud, and Namin, forming the Namin Khanate. His rule, and that of his children, over those areas, lasted a century, ending with the fall of the Qajars.[11] Persian Talish was also separated from the khanate, with Fath 'Ali Shah wanting to limit the power of Mir Mostafa Khan. He divided the area into 5 pieces (Karganrud, Asalem, Talesh-Dulab, Shandarmin, Masal) and created what came to be known as the Khamsa of Talesh (Persian: خمسهٔ طوالش, romanized: Khamsa-yī Ṭavālesh).[12][13]
In popular culture
The Talysh Khans proved a stimulating subject for famed Azeri poet-playwright Mirza Fath-Ali Akhundzadeh (1812–1878). A 1938 production of his The Adventures of the Vizier of the Lankaran's Khan (1851), starred the future president of Republic of Azerbaijan, Heydar Aliyev, then just a teenager.[14]
Rulers
| No. | Name | Lifespan | Took office | Left Office | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mir Jamal al-Din (Qara Khan) | 1708 – June/July 1787 | 1747 | June/July 1787 | [15] |
| 2 | Mir-Mostafa Khan | 1747 – 7 August 1814 | June/July 1787 | 7 August 1814 | [15] |
| 3 | Mir-Hasan Khan | 1784 – 12 July 1832 | August 1814 | June 1828 | [15] |
Footnotes
Notes
- ^ consisted of present-day Astara County and Astara District
- ^ Not be confused with the present-day Vilkij District of the Namin County, which is the namesake of the historical greater Vilkij
- ^ not exactly, but approximately the present-day Yardymli District
- ^ southern half of the present-day Masally District
- ^ northern half of the present-day Masally District
- ^ not exactly, but approximately the present-day Jalilabad District
- ^ not exactly, but approximately consisted of the present-day Parsabad, Bileh Savar and Germy counties and some parts of Bilasuvar District
References
- ^ Bournoutian 2016, p. xvii: "Serious historians and geographers agree that after the fall of the Safavids, and especially from the mid-eighteenth century, the territory of the South Caucasus was composed of the khanates of Ganja, Kuba, Shirvan, Baku, Talesh, Sheki, Karabagh, Nakhichivan and Yerevan, all of which were under Iranian suzerainty."
- ^ a b Tapper 1997, p. 161.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Shahvar & Abramoff 2018, p. 26.
- ^ Shahvar & Abramoff 2018, pp. 25–26.
- ^ Shahvar & Abramoff 2018, p. 43.
- ^ a b c Shahvar & Abramoff 2018, p. 27.
- ^ Khansuvarov 2011.
- ^ a b c Muradov 2019, p. 122.
- ^ Stuart Olsen et al. An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires Greenwood Publishing Group, 1 Jan. 1994 ISBN 978-0313274978 p 620
- ^ ru:Талышское ханство
- ^ Shahvar & Abramoff 2018, p. 41.
- ^ Asatrian, Garnik; Borjian, Habib (2005). "Talish and the Talishis (The State of Research)". Iran & the Caucasus. 9 (1): 45. ISSN 1609-8498.
- ^ Rabino, H. L. (1920). "Rulers of Gilan: Rulers of Gaskar, Tul and Naw, Persian Talish, Tulam, Shaft, Rasht, Kuhdum, Kuchisfahan, Daylaman, Ranikuh, and Ashkawar, in Gilan, Persia". The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland (3): 280–282. ISSN 0035-869X.
- ^ "7.4 Azerbaijan's President, Heydar Aliyev Interview in Azerbaijan International". www.azer.com.
- ^ a b c "Azerbaijan". www.worldstatesmen.org.
Sources
- Aydın, Mustafa (2016). "TALİŞ HANLIĞI" [Talish Khanate]. TDV İslâm Ansiklopedisi (in Turkish). Vol. EK–2. Istanbul: TDV İslâm Araştırmaları Merkezi. pp. 583–584. ISBN 978-975-3898-89-8.
- Bournoutian, George A. (2016). The 1820 Russian Survey of the Khanate of Shirvan: A Primary Source on the Demography and Economy of an Iranian Province prior to its Annexation by Russia. Cambridge: Gibb Memorial Trust. ISBN 9781909724808.
- Jafarov, Mayis (Spring 2012). "Taliş Xanliqinda ticarət əlaqələri və pul dövriyyasi" [Trade ties and money turnover in Talish Khanate]. TURAN (in Azerbaijani). 4 (14). Ankara: SAGE Publishing: 154–158 – via CEEOL.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|issue= - Khansuvarov, Razzaq (18 November 2011). "Yusiku Ocağı" [Monastery of Yusiku]. Tolışon Sədo [Voice of Talishis] (in Azerbaijani). No. 6. p. 3 – via talish.org.
- Muradov, Vidadi (2019). "Political and socio-economic history of Lankaran-Astara region of Azerbaijan (18th and early 20th centuries)". Azərbaycan Xalçaları [Azerbaijani Carpets]. 9 (28–29). Baku: Azer-Ilme: 118–139. ISSN 2304-330X.
- Poursafar Ghassabinejad, Ali (2010). خانات تالش [Talesh Khanate]. In Haddad-Adel, Gholam-Ali (ed.). Encyclopaedia of the World of Islam (in Persian). Vol. 14. Tehran: Encyclopaedia Islamica Foundation. ISBN 978-600-447015-5.
- Shahvar, Soli [in Persian]; Abramoff, Emil (2018). "The Khan, the Shah and the Tsar: The Khanate of Talesh between Iran and Russia". In Matthee, Rudi; Andreeva, Elena (eds.). Russians in Iran: Diplomacy and Power in the Qajar Era and Beyond. London: I.B. Tauris. pp. 24–48. ISBN 978-1-78673-336-8.
- Swietochowski, Tadeusz (1985). Russian Azerbaijan, 1905–1920: The Shaping of a National Identity in a Muslim Community. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-26310-7.
- Tapper, Richard (1997). Frontier Nomads of Iran: A Political and Social History of the Shahsevan. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-58336-5.
Further reading
- Ahmadi, Hossein (2005). تالشان: از دوره صفویه تا پایان جنگ دوم ایران و روس [The Talishis: From the Safavid Period till the End of the Second Russian-Persian War] (in Persian) (2nd ed.). Tehran: Iranian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. ISBN 964-361-326-7.
- Baddeley, John F. (1908). The Russian Conquest of the Caucasus. London: Longmans, Green and Company. OCLC 19250.
- Bakikhanov, Abbas Qoli Aqa (2009). The Heavenly Rose-Garden: A History of Shirvan and Daghestan. Translated by Willem Floor; Hasan Javadi. Washington, D.C.: Mage Publishers. ISBN 978-1-933823-27-0.
- Gmelin, Samuel Gottlieb (2007). Travels Through Northern Persia, 1770–1774. Translated by Willem Floor. Washington, D.C.: Mage Publishers. ISBN 978-1-933823-15-7.
- Petrushevsky, I. P. (1949). Очерки по истории феодальных отношений в Азербайджане и Армении в XVI-начале XIX вв [Outline of the History of Feudal Relations in Azerbaijan and Armenia from the XVI to the Beginning of the XIX Centuries] (PhD) (in Russian). Leningrad: Leningrad State University.
- Quliyev, C. B. [in Azerbaijani], ed. (1986). "Талышское ханство" [Talish Khanate]. Azerbaijani Soviet Encyclopedia (in Russian). Vol. IX. Baku: Azerbaijan National Academy of Sciences. p. 135.