Naval Base Woodlark Island
 United States Navy
United States Navy(1943-1945)
- v
- t
- e
- Pearl Harbor
- Marshalls–Gilberts raids
- K
- Doolittle Raid
- Midway
- Gilberts and Marshalls
- Marianas and Palau
- Volcano and Ryukyu
- Truk
- Ocean Island
- Japanese merchant raids
- Andaman Islands
- Homfreyganj massacre
- Christmas Island
- 1st Indian Ocean
- Ceylon
- Bay of Bengal
- 2nd Indian Ocean
- Indochina (1940)
- Franco-Thai War
- Thailand
- Malaya
- Hong Kong
- Singapore
- Indochina (1945)
- Malacca Strait
- Jurist
- Tiderace
- Zipper
- Strategic bombing (1944–45)
- Burma (1941–42)
- Burma (1942–43)
- Burma and India (1944)
- Burma (1944–45)
- Dutch East Indies (1941–42)
- Philippines (1941–42)
- RY
- Solomon Islands
- Coral Sea
- Timor
- Australia
- New Guinea
- New Britain
- Philippines (1944–45)
- Borneo (1945)
- North America
- Ellwood
- Aleutian Islands
- Estevan Point Lighthouse
- Fort Stevens
- Lookout Air Raids
- Fire balloon bombs
- Project Hula
- PX
- Air raids
- Mariana Islands
- Volcano and Ryukyu Islands
- Starvation
- Naval bombardments
- Sagami Bay
- South Sakhalin
- Kuril Islands
- Downfall
- Japanese surrender

Naval Base Woodlark Island was a United States Navy base built during World War II on Woodlark Island on Papua New Guinea. The US Navy built a PT boat base, boat repair depot, and harbor facilities at the city of Guasopa to support the Pacific War in 1943. The Harbor facilities was also built to support the US Navy in building the Narewa Airfield on the island. The base was part of the New Guinea campaign.[1][2]
History
On June 21, 1943, American forces came ashore on southern New Georgia, and then on June 30, landed on Woodlark Island as part of Operation Chronicle. Guasopa Bay lacked a usable dock so the landing were done with LST landing ships. Landing with the United States Army and United States Marine Corps at Guasopa was the US Navy's Seabee 60th Construction Battalion, and the 20th Construction. The 500 men with the 60th Construction Battalion started work on the airfield and its facilities. The 200 men with the 20th Construction Battalion started work on the harbor, barracks, mess halls, roads, water plant and other services.[1]
At Guasopa Bay Harbor at pontoon pier was built. The PT boat base, and boat repair depot was completed. A sawmill was built to supply lumber for the harbor and airfield needs. A coral quarry was built to build roads, walkways and runways.
Airfield construction started on July 2, after 12 days a 3,000-foot fighter plane runway was completed. On September 15, the runway was lengthened to 6,500-feet and bomber began use of the runway. The airfield was called Narewa Airfield, but also called Woodlark Island Airfield and Guasopa Airfield. After the war, the airfield became Guasopa Airport.[3]
Japan had airbases close enough that there were some bombings at Guasopa during construction. The bombings caused minor damage and no casualties to the construction crews.
All construction was completed on November 1, 1943, and the most Seabees depart Naval Base Woodlark Island. A maintenance crew of 309 men with the 60th Battalion stay at Naval Base Woodlark Island until March 1944.[1][4][5][6]
Naval Base Woodlark Island Feet Post Office, FPO# is 528 SF Woodlark Island.
See also
Gallery
-
 Camp Seabee Naval Base Brisbane building trips map
Camp Seabee Naval Base Brisbane building trips map -
 USS Achilles (ARL-41) in 1943 at Naval Base Woodlark Island
USS Achilles (ARL-41) in 1943 at Naval Base Woodlark Island -
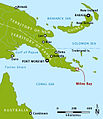 Naval Base Woodlark Island was supported by nearby Naval Base Milne Bay
Naval Base Woodlark Island was supported by nearby Naval Base Milne Bay -
 Map Naval Base Woodlark Island and Woodlark Harbor 1943
Map Naval Base Woodlark Island and Woodlark Harbor 1943 -
 Map Woodlark Island 1945
Map Woodlark Island 1945
References
- ^ a b c "Building the Navy's Bases, vol. 2 (part III, chapter 26)". US Navy.
- ^ "Pacific Wrecks - Woodlark Island (Muyua) Milne Bay Province, Papua New Guinea (PNG)". pacificwrecks.com.
- ^ "Pacific Wrecks - Narewa Airfield (Guasopa, Woodlark) Milne Bay Province, Papua New Guinea (PNG)". pacificwrecks.com.
- ^ "Pacific Wrecks - Fuel bowser truck parked at Narewa Airfield on Woodlark Island". pacificwrecks.com.
- ^ "60th NCB Woodlark Airfield 17". September 11, 2014 – via Flickr.
- ^ "Pacific Wrecks - Major Morris "Mike" Hecht in the cockpit of P-39 "Linnie" parked at Narewa Airfield on Woodlark Island". pacificwrecks.com.
External links
- youtube, Battle for New Guinea 1942-1945


















