Martín Yañéz Tafur
- Diego Díaz Tafur (father)
- Beatriz de Sotomayor (mother)
Juan Tafur
Hernán Venegas Carrillo
Pedro Fernández de Valenzuela
Martín Yañéz Tafur (?, Córdoba, Andalusia, Castile - ?, New Kingdom of Granada) was a Spanish conquistador who participated in the foundation of Cartagena, the Spanish conquest of the Muisca and the conquest of the Panche.
Biography
Martín Yañéz, also written as Yañés, Tafur was born in Córdoba, Andalusia, Spain with parents Diego Díaz Tafur and Beatriz de Sotomayor.[1][3] His father was the brother of Isabel Tafur, the mother of Juan Tafur, Martín's cousin. Other family included Hernán Venegas Carrillo and Pedro Fernández de Valenzuela, fellow conquistadors in Colombia.[4]
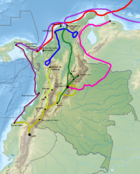
Yañéz Tafur left Spain for Trinidad in 1520, where he became mayor of the fortress Yuriparí. He left the Caribbean island for Cartagena de Indias, the city he helped founding with Pedro de Heredia in 1533. He accompanied De Heredia on further conquests to the west near the first Caribbean settlement San Sebastián de Urabá in present-day Antioquia. During this journey, Martín Yañéz Tafur returned the gold of Julián Gutiérrez to him upon release, soldier in the expedition who was imprisoned. This was seen as an act of great nobility in the greedy times of the Spanish conquests.[5] After this, Yañéz Tafur went south towards Cauca and from there inland towards the Bogotá savanna where he participated in the conquest of the Muisca and Panche, assisting his cousin Hernán Venegas Carrillo with the foundation of Tocaima in 1544.[2]
Yañés Tafur married Ines Ximeno de Bohorques, or Inés Jimeno de Bohórquez in Santa Fe de Bogotá and the couple had two sons; Martín Luis Yañes Tafur de Valenzuela and Francisco Tafur de Valenzuela.[1][3] His year and place of death are unknown.
See also
- List of conquistadors in Colombia
- Spanish conquest of the Muisca
- Pedro de Heredia, Hernán Venegas Carrillo
- Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada
References
- ^ a b c Martín Yañés Tafur - Geni
- ^ a b (in Spanish) Martín Yañéz Tafur - Banco de la República - Soledad Acosta Samper
- ^ a b (in Spanish) Martín Yañés Tafur
- ^ Rodríguez Freyle, 1638, p.62
- ^ Acosta, 1848, p.136
Bibliography
- Acosta, Joaquín. 1848. Compendio histórico del descubrimiento y colonización de la Nueva Granada en el siglo décimo sexto - Historical overview of discovery and colonization of New Granada in the sixteenth century, 1-460. Beau Press. Accessed 2017-03-06.
- Rodríguez Freyle, Juan, and Darío Achury Valenzuela. 1979 (1859) (1638). El Carnero - Conquista i descubrimiento del nuevo reino de Granada de las Indias Occidentales del mar oceano, i fundacion de la ciudad de Santa Fe de Bogota, 1-592. Fundacion Biblioteca Ayacuch. Accessed 2017-03-06.
Further reading
- De Castellanos, Juan. 1857 (1589). Elegías de varones ilustres de Indias, 1–567. Accessed 2017-03-01.
- Fernández de Piedrahita, Lucas. 1676. VI. Historia general de las conquistas del Nuevo Reino de Granada. Accessed 2017-03-01.
- Jiménez de Quesada, Gonzalo. 1576. Memoria de los descubridores, que entraron conmigo a descubrir y conquistar el Reino de Granada. Accessed 2017-03-01.
- Ocampo López, Javier. 1996. Leyendas populares colombianas - Popular Colombian legends, 1-384. Plaza y Janes Editores. Accessed 2017-03-01.
- De Plaza, José Antonio. 1810. Memorias para la historia de la Nueva Granada desde su descubrimiento el 20 de julio de 1810, 1-464. Imprenta del Neo-Granadino. Accessed 2017-03-01.
- Simón, Pedro. 1892 (1626). Noticias historiales de las conquistas de Tierra Firme en las Indias occidentales (1882-92) vol.1-5. Accessed 2017-03-01.
- N, N. 1979 (1889) (1539). Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada, 81-97. Banco de la República. Accessed 2017-03-01.
- v
- t
- e
Topics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
Geography and history | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||
Religion and mythology | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||
Caciques and neighbours | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||
Research and collections | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
 Category
Category