Löwenberger Land


Löwenberger Land is a municipality in the Oberhavel district, in the German state of Brandenburg, about 50 km north of Berlin.
Overview
Established on December 31, 1997, it consists of 15 villages:
|
|
|
Löwenberg was first mentioned in a 1269 deed, when it was acquired by the Bishopric of Brandenburg from the Brandenburg Margraves. A Gothic fieldstone church was erected in the 13th century. The church and large parts of the village were devastated by a fire in 1808. In 1877 Löwenberg gained access to the new Prussian Nordbahn railway line from Berlin to Neubrandenburg.
The municipality is known for Liebenberg Castle [de] (Schloss Liebenberg) built in 1745, the former residence of Philipp, Prince of Eulenburg (1847–1921) who from 1886 on held a homophile political salon - the Liebenberg Circle - here. Members included the Berlin military commander Kuno von Moltke, the later Chancellor Bernhard von Bülow and Emperor Wilhelm II. The circle broke up in 1907 with the Harden-Eulenburg Affair.
Transportation
Löwenberg is situated at the junction of the Bundesstraßen 96 and 167. The Löwenberg railway station is served by the Nordbahn line from Berlin to Stralsund. In east-west direction train connections are also available toward Prenzlau and Rheinsberg. Further Nordbahn railway stations are also in the villages of Grüneberg and Nassenheide.
Notable people
- Libertas Schulze-Boysen, Resistance fighter, born November 20, 1913, in Paris, died December 22, 1942, in Berlin Plötzensee Prison, granddaughter of Philipp zu Eulenburg, spent her childhood at Liebenberg Castle.
Some historical sites
- Some buildings and scenes from the region
-
 Church in Löwenberg
Church in Löwenberg -
 Church in Glambeck
Church in Glambeck -
 Church in Grieben
Church in Grieben -
 Church in Linde
Church in Linde -
 Sachsenhausen Todesmarsch (death march) route marker
Sachsenhausen Todesmarsch (death march) route marker -
 Church in Gutengermendorf
Church in Gutengermendorf -
 Building in Löwenberg
Building in Löwenberg -
 Former tavern in Gutengermendorf
Former tavern in Gutengermendorf - Liebenberg Castle
-
 Alcove house in Liebenberg
Alcove house in Liebenberg -
 Former schoolhouse in Klevesche Häuser
Former schoolhouse in Klevesche Häuser -
 Manor
Manor -
 Estate
Estate
Demography

-
 Development of Population since 1875 within the Current Boundaries (Blue Line: Population; Dotted Line: Comparison to Population Development of Brandenburg state; Grey background: Time of nazi rule -- Red background: Time of communist rule)
Development of Population since 1875 within the Current Boundaries (Blue Line: Population; Dotted Line: Comparison to Population Development of Brandenburg state; Grey background: Time of nazi rule -- Red background: Time of communist rule) -
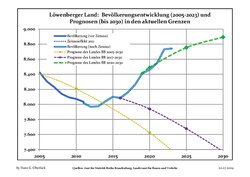 Recent Population Development and Projections (Population Development before Census 2011 (blue line); Recent Population Development according to the Census in Germany in 2011 (blue bordered line); Official projections for 2005-2030 (yellow line); for 2020-2030 (green line); for 2017-2030 (scarlet line)
Recent Population Development and Projections (Population Development before Census 2011 (blue line); Recent Population Development according to the Census in Germany in 2011 (blue bordered line); Official projections for 2005-2030 (yellow line); for 2020-2030 (green line); for 2017-2030 (scarlet line)
|
|
|
References
- ^ Landkreis Oberhavel Wahl der Bürgermeisterin / des Bürgermeisters, accessed 13 November 2022.
- ^ "Bevölkerungsentwicklung und Bevölkerungsstandim Land Brandenburg Dezember 2022" (PDF). Amt für Statistik Berlin-Brandenburg (in German). June 2023.
- ^ Detailed data sources are to be found in the Wikimedia Commons.Population Projection Brandenburg at Wikimedia Commons
External links

- Liebenberg Castle (in German)


























